Understanding Burned Gums from Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening, while a popular cosmetic procedure, can sometimes lead to unwanted side effects, with burned gums being a common concern. This occurs when the whitening agents, typically containing hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, come into contact with the soft tissues of the gums. The chemicals can cause irritation, inflammation, and in more severe cases, actual burns. Understanding the causes and how to treat burned gums is crucial for anyone considering or undergoing teeth whitening treatments. This guide provides comprehensive insights into managing and preventing this issue, ensuring a safer and more comfortable experience.
Causes of Gum Irritation from Whitening
The primary cause of gum irritation from teeth whitening is the contact of the whitening agent with the gum tissue. Several factors contribute to this. High concentrations of peroxide, often found in professional whitening treatments, can be more aggressive. Improper application techniques, such as using too much gel or not ensuring the trays fit snugly, can lead to the agent leaking onto the gums. Additionally, individuals with pre-existing gum sensitivity or those with gum recession are more susceptible. Overuse of whitening products, whether professional or at-home kits, can also increase the risk. Furthermore, the use of ill-fitting trays or trays that are not properly trimmed can cause the whitening solution to seep onto the gums, leading to irritation.
Chemical Burns vs. Other Types of Irritation
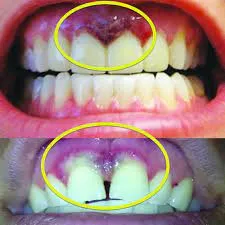
It’s important to differentiate between chemical burns and other types of gum irritation. Chemical burns from whitening agents are characterized by a distinct set of symptoms, often including a white or blanched appearance of the gums, followed by redness, swelling, and blistering. This contrasts with general irritation, which may present as redness, tenderness, and mild swelling without the characteristic blanching. Other types of irritation could be caused by an allergic reaction to the whitening product, or even mechanical irritation from the trays. Recognizing the specific type of irritation helps in determining the appropriate course of action. A chemical burn requires immediate attention to prevent further damage and promote healing.
Recognizing the Symptoms
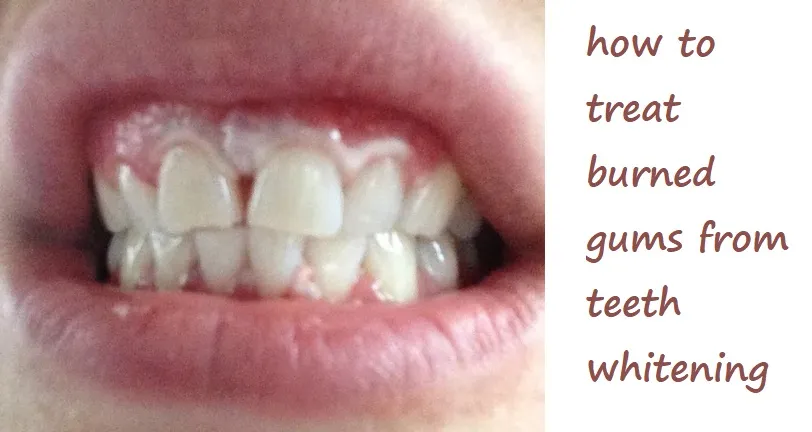
Early recognition of symptoms is vital for effective treatment. The first sign of gum irritation often includes a stinging or burning sensation, followed by redness and swelling. The gums may also appear white or blanched in the areas exposed to the whitening agent. Other symptoms can include increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks, as well as general discomfort when brushing or flossing. If the irritation is severe, the gums might develop blisters or ulcers. Pay close attention to your gums during and after whitening treatments to catch any early signs. Any unusual changes should be addressed promptly to prevent the issue from worsening and ensure a speedy recovery.
Immediate Signs of Burned Gums
The immediate signs of burned gums can be quite alarming. The first thing you might notice is a sharp, intense pain or burning sensation in the gums where the whitening agent made contact. The affected areas will quickly turn white or appear blanched due to the chemical reaction. This is often followed by redness, swelling, and sometimes the formation of blisters or ulcers. There might be a metallic taste in your mouth and increased saliva production. The gums might feel raw and tender to the touch. If you experience these immediate signs, it’s essential to stop the whitening treatment immediately and begin rinsing your mouth thoroughly with water to remove any remaining chemicals.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated Burns
If left untreated, burned gums can lead to more serious long-term effects. Chronic inflammation and irritation can damage the gum tissue, potentially leading to gum recession, where the gums pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots and increasing the risk of sensitivity and decay. Untreated burns can also increase the risk of developing gum disease (periodontitis). In severe cases, there could be a loss of gum tissue, affecting the aesthetics of your smile and, in extreme cases, could even impact the stability of your teeth. Therefore, it is important to seek professional care to prevent these issues from occurring and to ensure proper healing.
First Aid for Burned Gums
The first step is to stop the whitening treatment immediately. Rinse your mouth thoroughly with cool water for several minutes to dilute and remove any remaining whitening agent. Avoid vigorous brushing or flossing in the affected area. Gently apply a soothing agent like aloe vera gel or vitamin E oil to help reduce inflammation and promote healing. You can also use an over-the-counter pain reliever like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to manage any discomfort. If the pain is severe or if you see any blistering, seek professional dental care. Make sure to follow these initial steps to minimize damage and promote faster recovery.
Rinsing and Soothing Treatments
Rinsing your mouth with cool water is the initial and most important step in first aid. This helps to remove any lingering whitening agent and to soothe the irritated tissues. After rinsing, consider using a saltwater rinse (1/2 teaspoon of salt in 8 ounces of warm water) several times a day. Saltwater has natural antiseptic properties and can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Another soothing treatment is a diluted hydrogen peroxide rinse (3% hydrogen peroxide mixed with equal parts water), which can help prevent infection. Use these rinses gently, avoiding any harsh movements that could further irritate your gums. Follow the rinsing with a soft, gentle application of a soothing agent such as aloe vera.
Over-the-Counter Remedies
Several over-the-counter (OTC) remedies can provide relief for burned gums. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. Topical anesthetic gels containing benzocaine can provide temporary relief from pain, but should be used sparingly as they can numb the area and interfere with healing. Specialized mouthwashes designed for sensitive gums can also be beneficial, as they often contain ingredients that soothe irritation and promote healing. Avoid using mouthwashes containing alcohol, as they can further irritate the gums. Applying aloe vera gel directly to the affected area can provide a soothing effect and promote healing. Always read and follow the instructions on any OTC product to avoid any complications.
When to Seek Professional Dental Care
While some cases of burned gums can be managed at home, there are specific situations when professional dental care is essential. If the pain is severe and doesn’t subside after a few days, it’s time to see a dentist. If you notice significant blistering, ulceration, or signs of infection (such as increased swelling, pus, or fever), a dentist’s intervention is critical. Also, if the gum tissue is significantly damaged or if you experience any long-term changes in your gum health, seek professional advice immediately. A dentist can assess the extent of the damage, provide specialized treatments, and help prevent any long-term complications.
Professional Treatments for Severe Burns
Dentists have several treatment options for severe cases of burned gums. They might apply prescription-strength medications to reduce inflammation and promote healing. In cases of significant tissue damage, a dentist may recommend a protective barrier or dressing to cover the affected area and prevent further irritation. Antibiotics may be prescribed if there’s a risk of infection. In some cases, the dentist might perform a soft tissue graft to help repair the damaged gum tissue. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing and to address any potential complications.
Preventing Future Gum Irritation
Prevention is key to avoiding burned gums from teeth whitening. Always follow the instructions provided with the whitening product or by your dentist. Ensure that any custom-fitted trays fit snugly and don’t leak any whitening agent onto your gums. Before starting the whitening treatment, inform your dentist if you have a history of sensitive gums or gum recession. Limit the duration and frequency of whitening treatments, and never exceed the recommended usage. Consider using a lower concentration of the whitening agent, or if you are prone to sensitivity, discuss alternative methods with your dentist. Additionally, consider using a desensitizing toothpaste for a few weeks before beginning the whitening process to minimize sensitivity and reduce the likelihood of gum irritation.
Choosing the Right Whitening Products
Selecting the right whitening products can significantly reduce the risk of gum irritation. If you have sensitive gums, consult your dentist about products with lower concentrations of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. Consider professional whitening treatments, as your dentist can carefully monitor the process and protect your gums. For at-home kits, opt for products with FDA-approved safety seals and follow the instructions meticulously. Look for products specifically designed for sensitive teeth and gums. Avoid using products that contain abrasive ingredients, which can further irritate your gums. Always discuss your options with your dentist to find the most suitable and safest whitening product for your needs.
Proper Application Techniques
Proper application techniques are crucial to minimize the risk of gum irritation. Ensure that your teeth are clean and dry before applying any whitening agent. When using trays, be certain that they fit properly and cover only your teeth, not your gums. Use the amount of whitening gel recommended in the instructions, avoiding the temptation to use more, as this can increase the risk of leakage and irritation. If you are using strips, make sure they adhere to your teeth and avoid contact with your gums. After the recommended treatment time, remove the trays or strips and rinse your mouth thoroughly with water. Always brush gently and avoid aggressive flossing in the days following the whitening treatment to avoid further irritation.
Maintaining Healthy Gums After Whitening
Maintaining healthy gums after teeth whitening is vital to prevent future issues. Continue to practice good oral hygiene, including brushing twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing daily. Use a fluoride toothpaste to strengthen your enamel and protect your teeth. Regular dental check-ups are also essential, as your dentist can assess the health of your gums and teeth, and provide professional cleanings. Avoid smoking and excessive consumption of sugary drinks, as these can damage both your teeth and gums. Consider using a mouthwash that is specifically designed for gum health. If you experience any signs of irritation or bleeding, consult your dentist promptly for guidance.